Imagine this: you’re driving your new Tesla along a scenic California road when suddenly a nail punctures your tyre, leaving you stranded. You call for help, but the mechanic lacks the specialized tools for your car. This scenario highlights the importance of having the right tools for the job. Similarly, security analysts face challenges when they lack the right GRC tools in today’s rapidly evolving tech landscape. Here are the top GRC tools to help you stay ahead:

GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) tools are essential for streamlining business-critical processes such as policy management, risk assessment, legal compliance, and operational efficiency. Unlike traditional cybersecurity tools focusing solely on data security and privacy, GRC tools provide a broader scope by evaluating, tracking, measuring, and reporting risks across finance, strategy, and operations.
As businesses face increasing regulatory demands and complex risks, adopting the right GRC tools is critical for effective governance and compliance. These tools not only enhance visibility across an organization but also centralize security operations and improve collaboration between teams.
Read Also: OmniHuman-1: The New AI Model That Generates Realistic Video From a Photo
In this post, I’ll walk you through the Top 5 GRC Tools for 2025 that can help organizations tackle governance, dynamic risk management, and compliance challenges and explore other benefits. Additionally, I’ll outline key criteria for selecting the best GRC tools to fit your organization’s needs.
Table of Contents
What Are the Criteria for Selecting the Best GRC Tools?
How to Choose the Best GRC Tools
Benefits of Implementing GRC Tools
Common Challenges in Implementing GRC Tools
What are GRC tools?
GRC tools are purpose-built software that helps organizations provide a unified approach to governance, risk, and compliance (GRC).

Photo credit: jittawit
GRC tools help create and streamline business processes like policy management, risk assessment, ensure legal compliance, and streamline operations. GRC tools also involve a framework full suite of management capabilities where organizations can explore to develop, implement, and maintain effective processes and controls to ensure that requirements are consistently met and protections are always in the right place.
Well-functional GRC tools will help identify links in business processes, enforce internal controls, streamline operations, and secure sensitive data and protection in an organization.
| Governance
Composed of all the business processes and policies that are developed, implemented, and maintained to provide strategic directions and guidelines for day-to-day operations. |
Risk
Includes all activities related to monitoring, assessing, managing, and mitigating vulnerabilities to ensure that operations are not interrupted and that sensitive information is protected. |
Compliance
Tracks compliance rules, keeps impacted teams updated about changes, and sends alerts when systems, processes, or people put the organization at risk of non-compliance violations. |
|---|
Source: sailpoint.com
Key features for GRC tools
The best GRC tools include the following features and capabilities:
- Audit management
- Auditing tools
- Compliance database
- Content and document management
- Dashboard customization
- Ability for employees to access libraries, upload compliance evidence, and file and archive documents to avoid any compliance mistakes
- Analytics
- Asset management
Who uses GRC tools?
Organizations use GRC tools to support and enhance the requisite cross-functional collaboration across different departments, which enables them to meet requirements. GRC tools are of particular help in industries with strict regulations, including:
- Biotech and life sciences
- Energy and utilities
- Financial services
- Food and beverage
- Government
- Healthcare
- Higher education
- Insurance
- Manufacturing
- Retail
- Technology
- Transportation and logistics
Users of GRC tools span organizations and include:
- Senior executives to assess risks when making decisions
- Legal teams to help businesses avoid troubles that, in extreme cases, can result in jail time for executives
- Finance managers to support and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements
- Human resources executives to protect sensitive information
- IT departments to protect data from cyber threats
What Are the Criteria for Selecting the Best GRC Tools?
While choosing GRC tools might seem straightforward, selecting the right ones can be challenging. When choosing the best GRC tools for your business, start by determining your business objectives and assessing your requirements.
If you are looking to select the best GRC tools for your organization, here are the minimum criteria to consider when evaluating a GRC platform:
Assess Software Vendors and GRC Solutions
GRC software is available for on-site or hosted deployments. Pricing varies based on features and system requirements like data storage, disaster recovery, server availability, and network bandwidth. Launching a new GRC initiative with a modest investment in a GRC package may make sense, while an established program may require a more mature feature set. Note that GRC software with extensive features translates into a larger investment.
Automated Incident Management
Functional GRC tools should automate the incident response process, creating and applying rules that direct incidents to the proper channels and trigger remediation tactics. This automation benefits organizations by ensuring timely and effective incident handling. Tools should also make it easy to track response progress from a central dashboard and create an audit trail for analysis and compliance reporting.
Read Also: How DeepSeek, the Chinese AI, is Disrupting Global Tech: 5 Things You Should Know
Workflow
A good workflow engine is crucial for ensuring that work is distributed and monitored optimally. GRC workflows should align with those of organizations, as workflow disruptions can impact productivity and hinder adoption.
Customer Support
The efficacy of GRC tools depends largely on customer support during and after implementation. Important questions to ask when evaluating customer support include:
-
- What support is available if something breaks or is not working?
- What is the triage process for issues that go to support?
- Is there a dedicated support team?
- What is the availability of the support team?
- What service level agreements (SLAs) are available for support?
Deployment Options
While most organizations choose cloud-based GRC tools, confirming that on-premises options are available if required is essential. Understand how software updates and security patches are provided for on-premises deployments.
Document Management
GRC tools should provide strong document management to facilitate the organization and management of large amounts of documentation, including policies, standards, procedures, organizational controls, and test results. This helps ensure compliance and reduces administrative burdens.
Ease of Use
The best GRC tool will be easy to use and learn with minimal training for end users. Accessibility, how functions work together, and the platform’s intuitiveness are particularly important for encouraging user adoption.
Mobile Support
GRC tools must be accessible on all mobile devices to ensure flexibility and convenience for users.
Scalability
Evaluate GRC tools based on their ability to address modern needs and meet expanded requirements and teams. Scalability is crucial for growing organizations to ensure their GRC tools adapt to changing demands.
Security
A GRC platform should include critical security features like end-point encryption and IAM. Tools should also be available to identify and stop vulnerabilities and threats, protecting sensitive information.
Service Level Agreement (SLA) Management
A better GRC tool should prioritize functionality that makes it easy to manage SLA metrics and monitor minimum thresholds from one central location. This includes reporting capabilities to provide management with updates on the status and flag any issues. All SLAs should be linked to vendors and contracts, with automated alerts sent if risk indicators or performance lags are detected.
Vendor Oversight
GRC tools should help organizations assess vendors’ capacity to protect sensitive information. This is essential for ensuring that third-party vendors adhere to organizational security standards.
5 Best GRC Tools for 2025
LogicGate
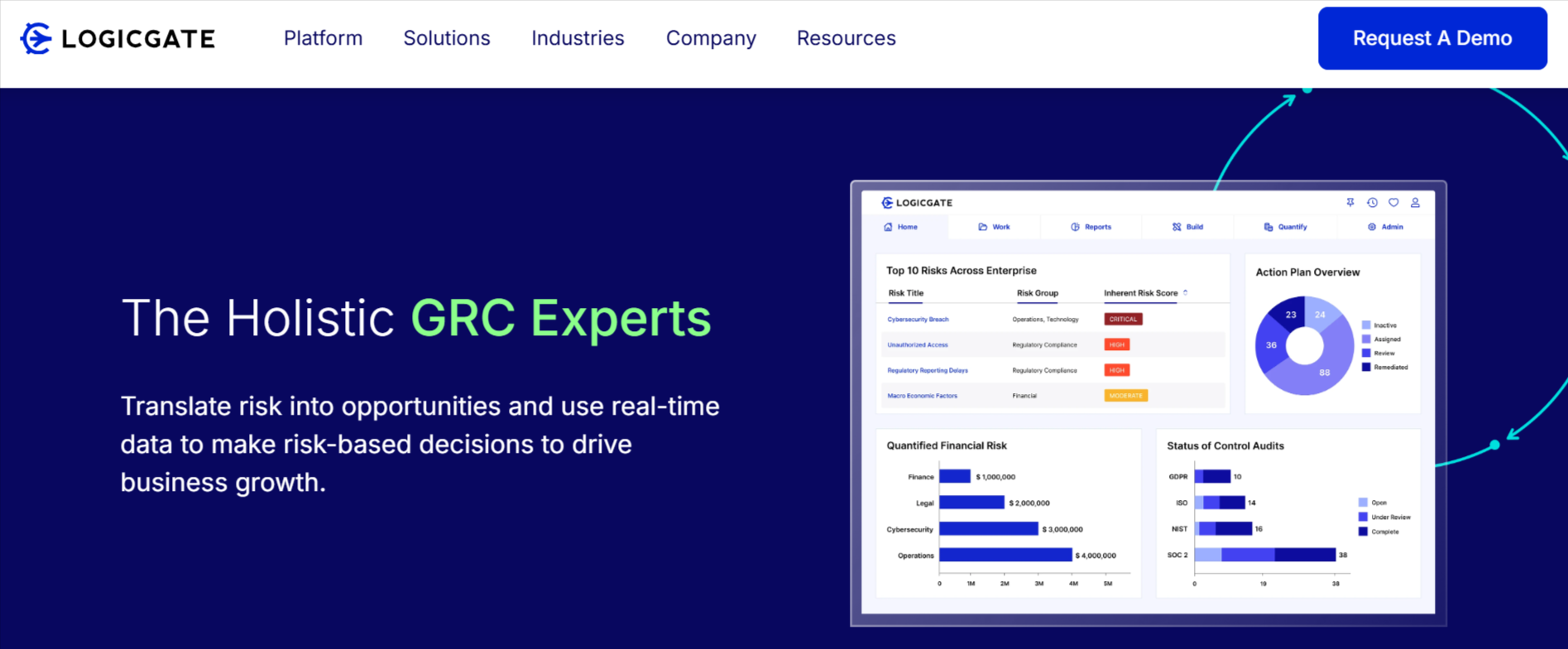
LogicGate offers a flexible, no-code platform that enables businesses to build custom workflows for risk management, compliance tracking, and policy enforcement.
Key Features:
Risk quantification and predictive analytics.
Vendor risk management and third-party assessments.
Drag-and-drop workflow automation.
MetricStream

MatricStream offers an efficient and effective integrated risk management and GRC (governance, risk management, and compliance) solution to help businesses manage risk and ensure organisational safety. It aligns with governance, risk management, and compliance, which are focused throughout the organization. MetricStream also involves three product lines – BusinessGRC, CyberGRC, and ESGRC – It aims to assist companies at every stage of their GRC journey. One final responsibility of the MetricStream is to help organization at every facet of the GRC
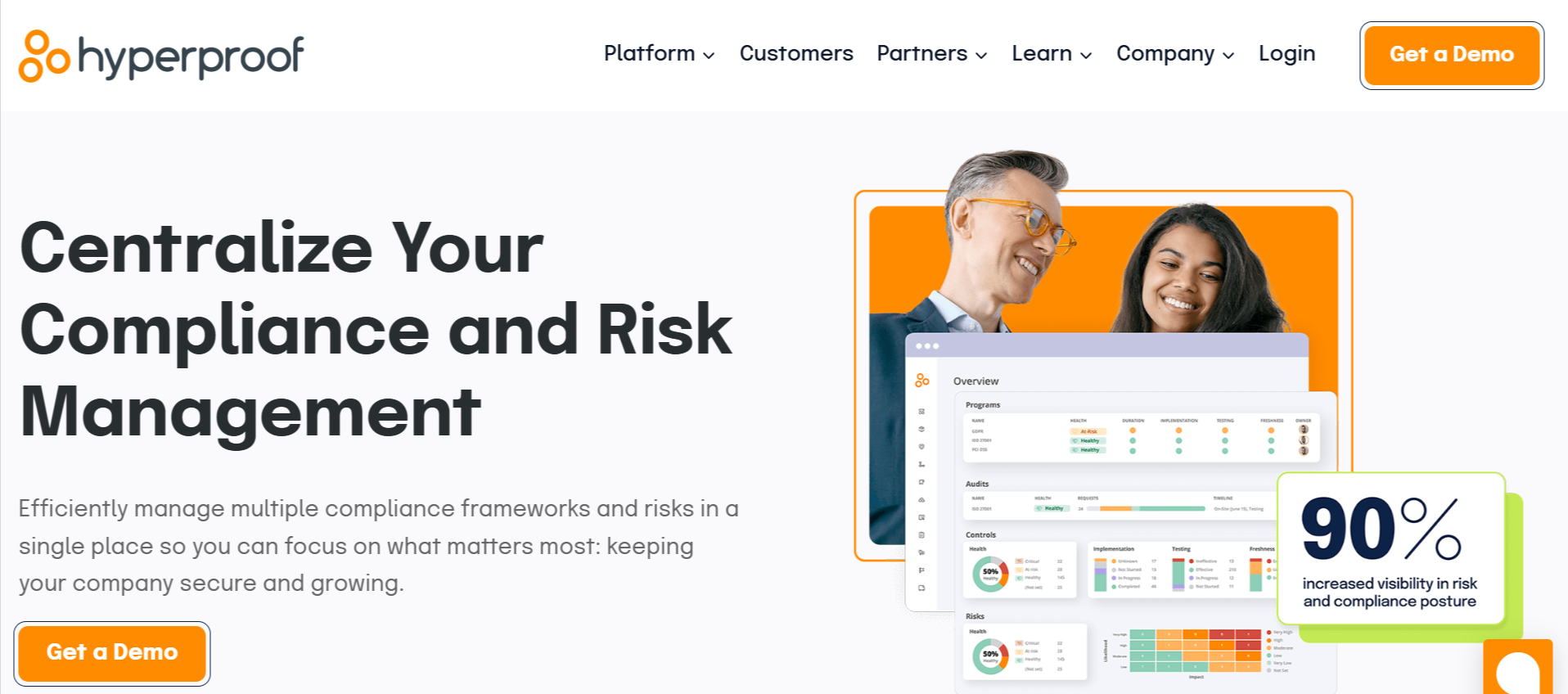
Hyperproof
Hyperproof helps organization effectively manage multiple frameworks and risks aimed at keeping your company secure and protected. It is one of the industry-leading compliance operations and risk management platforms. Hyperproof is a SaaS platform that empowers compliance, risk, and security teams to scale their workflows.
ServiceNow
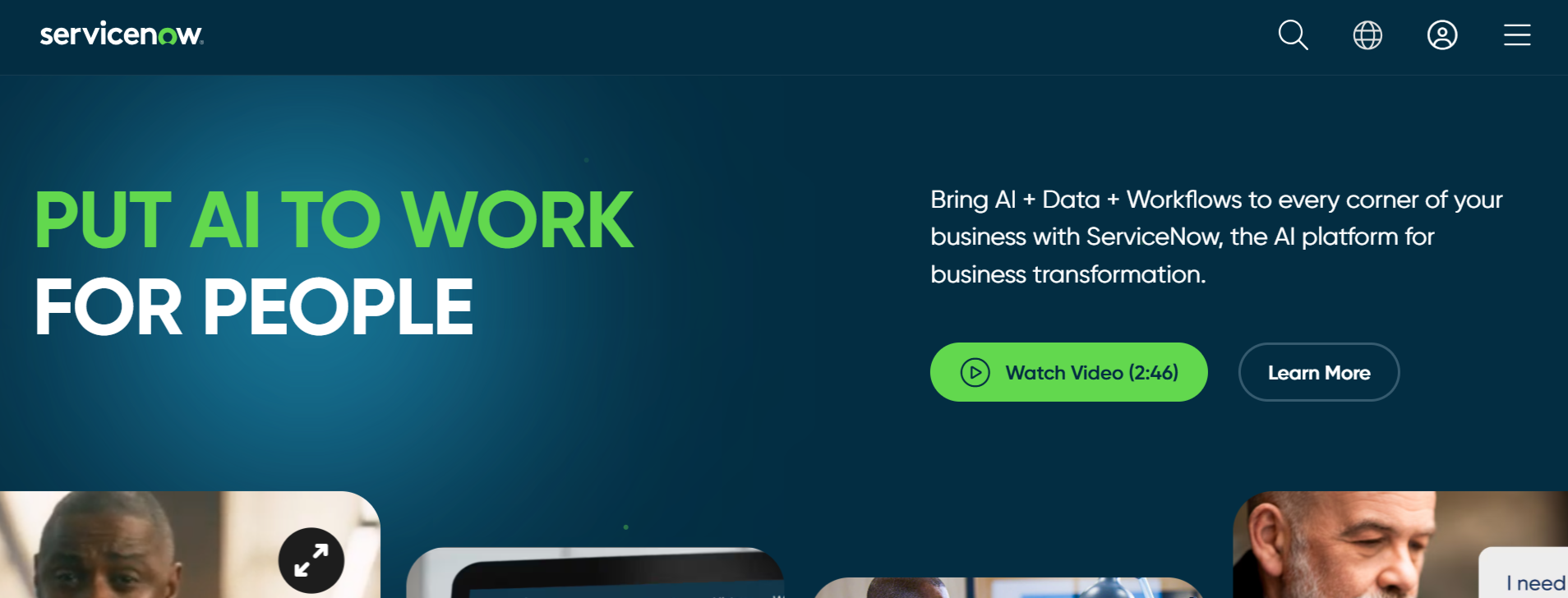
ServiceNow integrates seamlessly with IT operations, providing automated risk assessments, incident management, and policy compliance tracking.
Key Features:
IT risk and policy management dashboards.
Integration with ITSM, SIEM, and cloud security tools.
Automated compliance monitoring and reporting.
AuditBoard
AuditBoard offers a smart and efficient way of managing risk, compliance, and internal audit. This helps organization achieve greater efficiencies and inform business decisions.

According to research, AuditBoard is the leading cloud-based platform transforming how enterprises automate, collaborate, and report on risk. AuditBoard transforms how audit, risk, and compliance professionals manage today’s dynamic risk landscape with a modern, connected platform that engages the front to drive accelerated and informed decisions.
AuditBoard helps organizations simplify audit and risk management by offering evidence collection, automated tracking, and policy enforcement. It’s widely used in finance, healthcare, and the technology industry.
Key Features:
Automated audit workflows and risk tracking.
Integrated compliance management across frameworks.
Real-time risk insights and analytics.
How to Choose the Best GRC Tools
If you are considering choosing the best GRC tools, here are a few key aspects to consider:
Functionality
The choice of the best GRC tools depends on the functions you need. Ensure a balance of functionalities, including specialized tools like dedicated risk management. Determine must-have features before proceeding, as the range of options can be overwhelming.
Integration
It is important to understand how well a GRC tool integrates with your existing systems. For example, if you already use project management or document control tools, you may need a GRC solution that integrates seamlessly. Seamless integration ensures easy data transfer between systems and a consistent user experience.
Configurability
Look for a platform that can meet your requirements. Features like flexible workflow automation, customizable dashboards, and the ability to define custom fields are crucial. It is better to choose a tool that can be tailored to fit your needs.
User-Friendly
Choosing tools that are intuitive and easy to use is essential for smooth user adoption and frontline engagement in GRC. User-friendly tools with logical sequencing of tasks make it easier for frontline executives to report observations, issues, or anomalies, which can then be analyzed by the second line.
Pricing
Lastly, consider the costs. GRC software is available at various prices, from free, open-source options to enterprise-level subscriptions. Consider the number of users and whether you prefer cloud-based or on-premise deployment.
Benefits of Implementing GRC Tools
Implementing effective and robust GRC tools provides organizations with a comprehensive view of risks, controls, and compliance data, enabling informed decision-making for executives. It also helps automate compliance monitoring and risk detection, allowing organizations to address potential policy breaches proactively.
Enhanced accountability and transparency are achieved by streamlining workflows, optimizing resource allocation, and reducing operational redundancies. Here are some benefits of implementing a GRC tool:
Refined Decision-Making Capabilities
A GRC platform offers executives and stakeholders a comprehensive view of risks, controls, and compliance issues. With all this information in one place, leaders can make well-informed decisions based on data rather than assumptions.
Enhanced Compliance and Reduced Risk
A practical and effective GRC tool automates compliance monitoring and reporting. It also provides alerts to potential policy violations and risks, allowing organizations to address issues before they become violations.
Augmented Accountability and Transparency
GRC tools enhance accountability by providing each employee with visibility into relevant risks, controls, and compliance issues. This clarity helps employees understand their roles and responsibilities, receive guidance on fulfilling them, and demonstrate compliance via automated reporting.
Optimized Processes and Resource Efficiency
Integrating GRC tools into workflows streamlines processes by providing a centralized platform for managing risk and compliance activities. This centralization eliminates the need for disparate systems and manual processes, reducing duplication of efforts and saving valuable time and resources.
Increased Operational Efficiency
Implementing GRC tools leads to increased operational efficiency by automating tasks, reducing manual errors, and improving overall workflow management.
Stronger Governance and Strategic Alignment
GRC tools help align organizational strategies with governance and compliance requirements, ensuring that business objectives are met while maintaining regulatory adherence.
Common Challenges in Implementing GRC Tools
Implementing GRC tools involves overcoming potential roadblocks. Here are some common challenges organizations face:
Resistance to Change
Some common obstacles in implementing GRC tools stem from resistance to change among employees accustomed to existing processes. Overcoming this resistance requires effective change management strategies, such as stakeholder engagement, clear communication, and comprehensive training programs to ensure organizational buy-in and adoption.
Resource Constraints
Limited resources, such as budgetary constraints and inadequate staffing, can hinder the successful implementation of GRC tools. Organizations must allocate adequate resources by prioritizing GRC initiatives and securing necessary funding and personnel to achieve successful implementation.
Complexity of Regulations
Regulatory requirements pose a significant challenge for organizations implementing GRC tools. Ensuring that GRC tools adequately address regulatory compliance requirements and adapt to evolving regulations requires careful planning, specialized expertise, and ongoing monitoring and updates to stay compliant.
Integration Challenges
Integration challenges with existing systems and processes are another major obstacle in implementing GRC tools. Because GRC tools may need to interface with various platforms and databases, careful planning and execution are required to ensure smooth and seamless integration without disrupting ongoing operations.
Conclusion
Just as a mechanic without tools struggles to work and access certain areas of a faulty motor engine, an organization without proper security tools, such as GRC tools, will face similar challenges. When an organization adopts a GRC tool, it helps mitigate risks, enhance control, and manage compliance data, enabling executives to make informed decisions. Moreover, having an efficient GRC tool accelerates organizational growth and ensures seamless regulatory compliance.
Read Also: What are the 7 Best GRC Courses for 2025
GRC Tools FAQ
What is a GRC framework?
A GRC framework is a structured approach that integrates governance, risk management, and compliance.
What is a GRC roadmap?
A GRC roadmap outlines the steps and components required to implement the plans and strategies outlined in a GRC framework, often including a timeline or milestones.
What is the difference between GRC and cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity protects organizations’ systems, networks, devices, and data. GRC provides the framework and tools to integrate these protections into organizational processes and ensure that organizational goals and objectives are achieved.
Why does GRC fail?
In some cases, GRC programs fail due to inadequate GRC tool performance. More often, GRC implementations fail due to a lack of strategy, insufficient planning, and faulty implementation.
What are the types of risk in GRC?
The most commonly used risk categories include:
- Strategic
- Financial
- Operational
- People
- Regulatory
What are the key focus areas for GRC tools?
- Corrupt and illegal practices
- Privacy and data breaches
- Employee behavior
- Environmental and sustainability concerns
- Health and Safety
- Process risks
Who is part of a GRC implementation?
- Organization’s board or governing body
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO)
- Risk manager
- Compliance manager
- Internal audit manager
- Chief Information Officer (CIO)
